You have no items in your shopping cart.
V5 Epitope Tag antibody
Catalog Number: orb345390
| Catalog Number | orb345390 |
|---|---|
| Category | Antibodies |
| Description | V5 Epitope Tag antibody |
| Species/Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Tested applications | ELISA, IHC, WB |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Immunogen | This antibody was purified from whole rabbit serum prepared by repeated immunizations with V5 epitope tag peptide corresponding to aa 95-108 of the V protein conjugated to KLH using maleimide. |
| Concentration | 1.8 mg/mL |
| Dilution range | ELISA: 1:10,000 - 1:60,000, IHC: 1:500 - 1:3,000, WB: 1:5,000 - 1:10,000 |
| Form/Appearance | Liquid (sterile filtered) |
| Purity | This affinity-purified antibody is directed against V5 motif and is useful in determining its presence in various assays. This polyclonal anti-V5-tag antibody detects over-expressed proteins containing the V5 epitope tag. To date this antibody has reacted with all V5 tagged proteins tested so far. In western blotting of bacterial extracts the antibody does not cross-react with endogenous proteins. The antibody recognizes the V5-epitope tag (GKPIPNPLLGLDST) fused to either the carboxy- terminal end of targeted proteins in transfected or transformed cells. Although not yet tested, expect reactivity with recombinant proteins prepared with the V5-epitope tag fused to the amino terminal end as well. |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| NCBI | 55775699 |
| Storage | Store vial at -20° C prior to opening. Aliquot contents and freeze at -20° C or below for extended storage. Avoid cycles of freezing and thawing. Centrifuge product if not completely clear after standing at room temperature. This product is stable for several weeks at 4° C as an undiluted liquid. Dilute only prior to immediate use. |
| Buffer/Preservatives | 0.01% (w/v) Sodium Azide |
| Alternative names | Rabbit Anti-V5 Epitope Tag Antibody, Rabbit Anti V Read more... |
| Note | For research use only |
| Application notes | Anti-V5 is optimally suited for monitoring expression of V5-tagged fusion proteins. The V5 epitope tag is derived from a small epitope (Pk) present on the P and V proteins of the paramyxovirus of simian virus 5 (SV5). The V5 tag is usually used with all 14 amino acids (GKPIPNPLLGLDST), although it has also been used with a shorter 9 amino acid sequence (IPNPLLGLD). This antibody has been tested by ELISA and western blotting against both the immunizing peptide and V5 containing recombinant proteins. Although not tested, this antibody is likely functional for immunoprecipitation and immunocytochemistry. |
| Expiration Date | 12 months from date of receipt. |

Anti-V5 epitope tag polyclonal antibody detects V5-tagged recombinant protein by western blot. This antibody was used at 1.0 µg/ml to detect 0.05 µg (lane 2) of full-length recombinant mouse serum albumin containing the V5 epitope tag at the carboxy end. Comparison to MW markers (lane 1) indicates detection of monomeric V5 tagged albumin. A 4-20% gradient gel was used to separate the protein by SDS-PAGE under non-reducing conditions. The protein was transferred to nitrocellulose using standard methods. After blocking the membrane was probed with the primary antibody overnight at 4°C followed by washes and reaction with a 1:10000 dilution of IRDye 800 conjugated Gt-a-Rabbit IgG [H&L] for 45 min at room temperature.
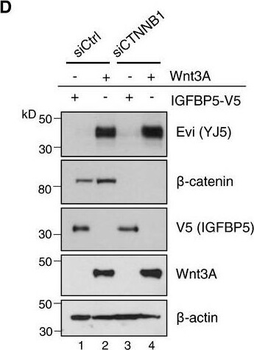
Evi is not transcriptionally regulated by WntA, BFPKM‐normalized RNA‐seq. The distribution into tumor and healthy samples was based on their barcodes as described in TCGA Wiki. Statistical significance of gene expression differences was determined using a Student's t‐test under the alternative hypothesis H1 that gene expression is higher in tumors compared to healthy tissue. The boxplot diagram shows the median as line within the box, the 25th and 75th percentiles as the upper and lower part of the box, the 10th and 90th percentiles as error bars and outliers as circles.CHEK293T cells were transfected with the indicated expression constructs, treated with 100 ng/mL recombinant mouse Wnt3A (rec. W3A) or with 10 μM GSK3 inhibitor SB216763 for the indicated hours (h). AXIN2 and Evi mRNA levels were analyzed by qRT–PCR and normalized to GAPDH expression. Results are shown as mean ± s.d. from three independent experiments. D, D'Twenty‐four hours after reverse transfection with Ctrl or CTNNB1 siRNA, HEK293T cells were transfected with Wnt3A or IGFBP5‐V5 expression plasmids and analyzed (D) for the indicated proteins via immunoblotting or (D') for canonical Wnt activity using the TCF‐Luciferase Wnt reporter assay. Immunoblotting is representative of three independent experiments, and Wnt reporter activity was calculated as mean from three independent experiments ± s.d.
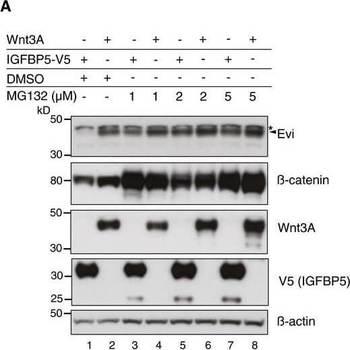
Evi poly‐ubiquitination is regulated by the presence of Wnt proteinsHEK293T cells were transfected with Wnt3A or IGFBP5‐V5 expression constructs and treated with MG132 at the indicated concentrations for 24 h. Cell lysates were analyzed for endogenous Evi by immunoblotting. Total β‐catenin protein was used to assess MG132 efficiency. Wild‐type (wt), stable Wnt3‐expressing, or EviKO2.9 HEK293T cells were treated with 1 μM MG132 for 24 h. TUBE2 immunoprecipitates were assayed for endogenous Evi or K48 poly‐ubiquitin by immunoblotting. To confirm specificity of the TUBE2 assay, Ctrl agarose beads were used as control. The asterisk at the β‐actin blot indicates Wnt3A proteins blotted before membrane stripping. Scheme illustrating ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of Evi, which is blocked in the presence of Wnt ligands. HEK293T cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids and additionally treated with 5 μM LGK974 for 48 h when indicated. In case of Wnt3A‐KDEL, the ER‐retaining sequence KDEL was C‐terminally fused to Wnt3A. Dvl2‐HA, Dvl3, and β‐catenin‐YFP overexpression was used as negative control to verify that Evi stabilization was not due to downstream activation of Wnt signaling. All Western blots are representative of three independent experiments. β‐Actin was used as loading control. Specific Evi bands are marked by arrows and unspecific bands by asterisks.
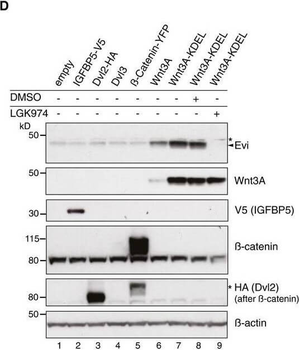
Evi poly‐ubiquitination is regulated by the presence of Wnt proteinsHEK293T cells were transfected with Wnt3A or IGFBP5‐V5 expression constructs and treated with MG132 at the indicated concentrations for 24 h. Cell lysates were analyzed for endogenous Evi by immunoblotting. Total β‐catenin protein was used to assess MG132 efficiency. Wild‐type (wt), stable Wnt3‐expressing, or EviKO2.9 HEK293T cells were treated with 1 μM MG132 for 24 h. TUBE2 immunoprecipitates were assayed for endogenous Evi or K48 poly‐ubiquitin by immunoblotting. To confirm specificity of the TUBE2 assay, Ctrl agarose beads were used as control. The asterisk at the β‐actin blot indicates Wnt3A proteins blotted before membrane stripping. Scheme illustrating ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of Evi, which is blocked in the presence of Wnt ligands. HEK293T cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids and additionally treated with 5 μM LGK974 for 48 h when indicated. In case of Wnt3A‐KDEL, the ER‐retaining sequence KDEL was C‐terminally fused to Wnt3A. Dvl2‐HA, Dvl3, and β‐catenin‐YFP overexpression was used as negative control to verify that Evi stabilization was not due to downstream activation of Wnt signaling. All Western blots are representative of three independent experiments. β‐Actin was used as loading control. Specific Evi bands are marked by arrows and unspecific bands by asterisks.
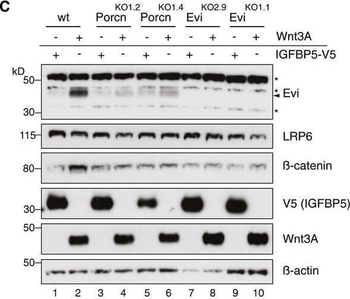
Evi stabilization is dependent on Wnt palmitoylation. Schematic illustration of the Porcn‐mediated Wnt palmitoylation, which is important for Evi‐Wnt interaction and which is blocked upon Porcn inhibition (LGK974), in PorcnKO cells and by using a palmitoylation‐deficient S209A Wnt3A mutant. Wild‐type or stable Wnt3‐and Wnt5B‐expressing HEK293T cells were treated with 5 μM LGK974 for 48 h and subjected to Western blot analysis. Western blot analysis of endogenous Evi in wt, PorcnKO, or EviKO HEK293T cells upon overexpression of Wnt3A or IGFBP5‐V5. PorcnKO1.2 and PorcnKO1.4 indicate clone #2 and clone #4 of PorcnKO HEK293T cells generated with Porcn sgRNA1 (Appendix Fig S3). Clonal EviKO HEK293T cells were generated with Evi sgRNA2 (EviKO2.9; clone #9) or Evi sgRNA1 (EviKO1.1; clone #1; Appendix Fig S2). Increase in total β‐catenin protein served as control for Wnt pathway activation. Western blot analysis of endogenous Evi in HEK293T cells transfected with the indicated overexpression plasmids. When indicated, the cells were additionally treated with 5 μM LGK974 for 48 h. Western blot analysis of endogenous Evi in HCT116 or A375 cells treated with 5 μM LGK974 or DMSO for the indicated hours (h). All Western blots are representative of three independent experiments. β‐Actin was used as a loading control, LRP6 as a reference membrane protein and EGF‐Myc and IGFBP5‐V5 as controls for secreted proteins. Specific Evi bands are indicated by arrows, and unspecific bands are marked by asterisks. Scheme: Wnt‐induced Evi stabilization is blocked in the absence of Wnt palmitoylation (PorcnKO, LGK974, Wnt3A S209A).
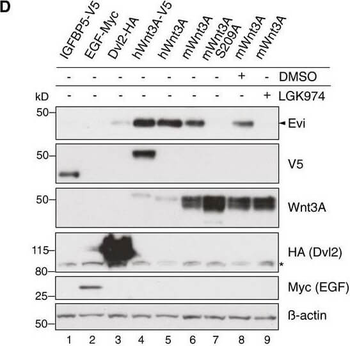
Evi stabilization is dependent on Wnt palmitoylation. Schematic illustration of the Porcn‐mediated Wnt palmitoylation, which is important for Evi‐Wnt interaction and which is blocked upon Porcn inhibition (LGK974), in PorcnKO cells and by using a palmitoylation‐deficient S209A Wnt3A mutant. Wild‐type or stable Wnt3‐and Wnt5B‐expressing HEK293T cells were treated with 5 μM LGK974 for 48 h and subjected to Western blot analysis. Western blot analysis of endogenous Evi in wt, PorcnKO, or EviKO HEK293T cells upon overexpression of Wnt3A or IGFBP5‐V5. PorcnKO1.2 and PorcnKO1.4 indicate clone #2 and clone #4 of PorcnKO HEK293T cells generated with Porcn sgRNA1 (Appendix Fig S3). Clonal EviKO HEK293T cells were generated with Evi sgRNA2 (EviKO2.9; clone #9) or Evi sgRNA1 (EviKO1.1; clone #1; Appendix Fig S2). Increase in total β‐catenin protein served as control for Wnt pathway activation. Western blot analysis of endogenous Evi in HEK293T cells transfected with the indicated overexpression plasmids. When indicated, the cells were additionally treated with 5 μM LGK974 for 48 h. Western blot analysis of endogenous Evi in HCT116 or A375 cells treated with 5 μM LGK974 or DMSO for the indicated hours (h). All Western blots are representative of three independent experiments. β‐Actin was used as a loading control, LRP6 as a reference membrane protein and EGF‐Myc and IGFBP5‐V5 as controls for secreted proteins. Specific Evi bands are indicated by arrows, and unspecific bands are marked by asterisks. Scheme: Wnt‐induced Evi stabilization is blocked in the absence of Wnt palmitoylation (PorcnKO, LGK974, Wnt3A S209A).
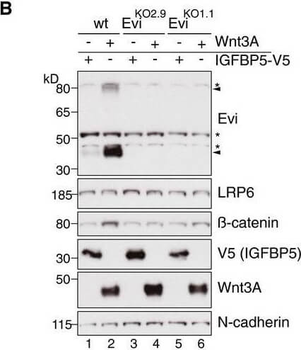
Wnt ligand production increases Evi protein levels In situ RNA hybridization (red dots) and immunohistochemistry (brown staining) of Evi were performed on sequential FFPE tissue slides of healthy colon and matched colon cancer tissue from five patients. The illustrated example is representative for three patients. Scale bar: 40 μm. Specificity of Evi probes was confirmed in Appendix Fig S1B. Wild‐type (wt) or EviKO HEK293T cells were transfected with Wnt3A or IGFBP5‐V5 expression plasmids and subjected to Western blot analysis. Specific Evi bands are indicated by arrows and unspecific bands by asterisks. Endogenous Evi is not only detectable as a monomeric form (46 kDa) but also as SDS‐resistant dimers (80 kDa). Clonal EviKO HEK293T cells were generated via CRISPR/Cas9 using Evi sgRNA #2 (EviKO2.9) or Evi sgRNA #1 (EviKO1.1; Appendix Fig S2). HEK293T cells were transfected with Wnt expression plasmids and analyzed for endogenous Evi levels by immunoblotting with a mouse monoclonal Evi antibody (Biolegend, clone YJ5). HEK293T cells were transfected with the indicated overexpression constructs, treated with 100 ng/mL recombinant mouse Wnt3A (rec. W3A) or with 10 μM GSK3β inhibitor SB216763 for the indicated hours (h). The obtained cell lysates were used for Western blot analysis. Representative Western blots of three independent experiments are shown. β‐Actin or N‐cadherin were used as a loading control, and LRP6 served as a reference membrane protein. Scheme showing that Evi is regulated through Wnt proteins within the Wnt‐producing cell. Canonical Wnt signaling can be activated by Wnt ligands, Dishevelled (Dvl) overexpression or by the GSK3β inhibitor SB216763.
Filter by Rating
- 5 stars
- 4 stars
- 3 stars
- 2 stars
- 1 stars








