You have no items in your shopping cart.
Recombinant human LIF protein (HEK293)
Catalog Number: orb1516392
| Catalog Number | orb1516392 |
|---|---|
| Category | Proteins |
| Description | Recombinant human LIF protein (HEK293) |
| Tag | Tag free |
| Concentration | >0.5 mg/ml |
| Form/Appearance | Lyophilized |
| Purity | > 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE; > 95% as determined by SEC-HPLC |
| MW | Due to glycosylation, the protein migrates to 40-55 kDa based on Tris-Bis PAGE result. |
| Target | Leukemia inhibitory factor |
| Protein Sequence | 23-202/202 |
| Expression System | HEK293 cell |
| Biological Activity | Not tested |
| Endotoxins | < 1.0 EU/μg as determined by LAL |
| Storage | Stored at -70°C or -20°C. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Buffer/Preservatives | Lyophilized from 0.22um filtered solution in PBS (pH7.4) with 5mM DTT. Normally 5% trehalose is added as protectant before Lyophilization. |
| Alternative names | Leukemia inhibitory factor; DIA; CDF; Cholinergic Read more... |
| Note | For research use only |
| Application notes | Centrifuge tubes before opening. Reconstituting to a concentration more than 100 μg/ml is recommended. Dissolve the lyophilized protein in distilled water. |
| Expiration Date | 6 months from date of receipt. |

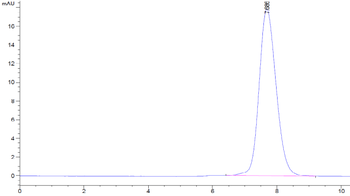
Human LIF Protein on Tris-Bis PAGE under reduced condition. The purity is greater than 95%.
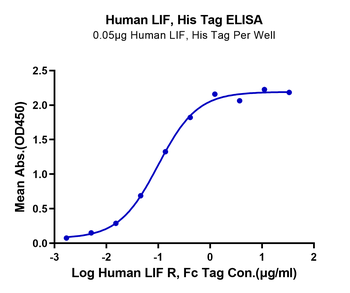
Immobilized Human LIF at 0.05 µg/ml (100 µl/Well). Dose response curve for Human LIF R, Fc Tag with the EC50 of 99.3 ng/ml determined by ELISA.
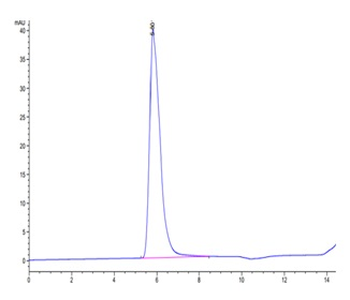
The purity of Human LIF Protein is greater than 95% as determined by SEC-HPLC.
Recombinant human LIF R protein, C-hFc (HEK293) [orb1516391]
> 95% as determined by Tris-Bis PAGE; > 95% as determined by SEC-HPLC
Due to glycosylation, the protein migrates to 120-140 kDa based on Tris-Bis PAGE result.
50 μggp130/IL6ST Protein, Human, Recombinant (His) [orb1960481]
98.00%
68.94 kDa (predicted). Due to glycosylation, the protein migrates to 80-110 kDa based on Tris-Bis PAGE result.
500 μg, 100 μg, 1 mgLIF Protein, Human, Recombinant (His) [orb1956179]
97.90%
21.2 kDa (predicted); 35-42 kDa (reducing conditions)
100 μg, 200 μg, 500 μgLIF Protein, Human, Recombinant (hFc) [orb1956156]
98.00%
46.7 kDa (predicted); 63 kDa (reducing conditions)
100 μgLIF Protein, Human, Recombinant [orb1955622]
SDS-PAGE: 99.5%; SEC-HPLC: 98.8%
19.7 kDa (predicted); 23-43 kDa (reducing condition, due to glycosylation)
20 μg, 100 μg