You have no items in your shopping cart.
Cart summary
Item 1 of 1
Human TNF protein
Catalog Number: orb594841
| Catalog Number | orb594841 |
|---|---|
| Category | Proteins |
| Description | Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor(TNF),partial (Active) |
| Tag | C-terminal 6xHis-tagged |
| Form/Appearance | Lyophilized powder |
| Purity | Greater than 95% as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| MW | 18.5 kDa |
| UniProt ID | P01375 |
| Protein Sequence | VRSSSRTPSDKPVAHVVANPQAEGQLQWLNRRANALLANGVELRDNQLVVPSEGLYLIYSQVLFKGQGCPSTHVLLTHTISRIAVSYQTKVNLLSAIKSPCQRETPEGAEAKPWYEPIYLGGVFQLEKGDRLSAEINRPDYLDFAESGQVYFGIIAL |
| Protein Length | Partial |
| Source | E.coli |
| Biological Origin | Homo sapiens (Human) |
| Biological Activity | The ED50 as determined in a cytotoxicity assay using L‑929 mouse fibroblast cells in the presence of the metabolic inhibitor actinomycin D is 10-40 pg/ml. |
| Expression Region | 77-233aa |
| Endotoxins | Less than 1.0 EU/µg as determined by LAL method. |
| Storage | The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself. Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20℃/-80℃. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20℃/-80℃. |
| Buffer/Preservatives | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered 20 mM PB, 150 mM NaCl, pH 7.4 |
| Alternative names | Tumor Necrosis Factor; Cachectin; TNF-Alpha; Tumor Read more... |
| Background | Tumor Necrosis Factor-α (TNF-α) is secreted by macrophages, monocytes, neutrophils, T-cells, and NK-cells following stimulation by bacterial LPS. Cells expressing CD4 secrete TNF-α while cells that express CD8 secrete little or no TNF-α. Synthesis of TNF-α can be induced by many different stimuli including interferons, IL2, and GM-CSF. The clinical use of the potent anti-tumor activity of TNF-α has been limited by the proinflammatory side effects such as fever, dose-limiting hypotension, hepatotoxicity, intravascular thrombosis, and hemorrhage. Designing clinically applicable TNF-α mutants with low systemic toxicity has been of intense pharmacological interest. Human TNF-α that binds to murine TNF-R55 but not murine TNF-R7, exhibits retained anti-tumor activity and reduced systemic toxicity in mice compared with murine TNF-α, which binds to both murine TNF receptors. Based on these results, many TNF-α mutants that selectively bind to TNF-R55 have been designed. These mutants displayed cytotoxic actitumor cell lines in vitro and have exhibited lower systemic toxicity in vivo. Recombinant Human TNF-α High Active Mutant differs from the wild-type by amino acid subsitution of amino acids 1-7 with Arg8, Lys9, Arg10 and Phe157. This mutant form has been shown to have increased activity with less inflammatory side effects in vivo |
| Note | For research use only |
| Application notes | Partial |
| Expiration Date | 6 months from date of receipt. |

(Tris-Glycine gel) Discontinuous SDS-PAGE (reduced) with 5% enrichment gel and 15% separation gel.
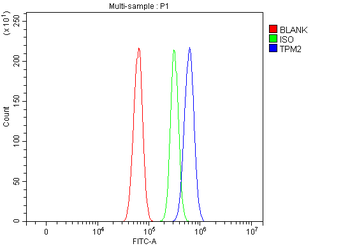
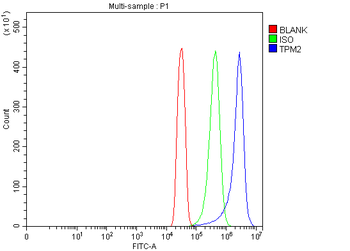
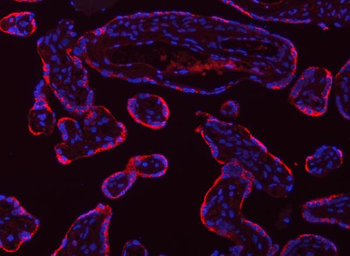
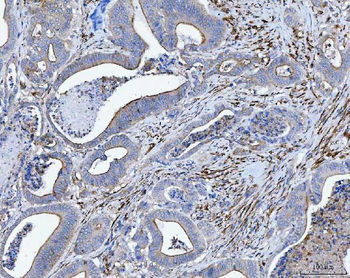
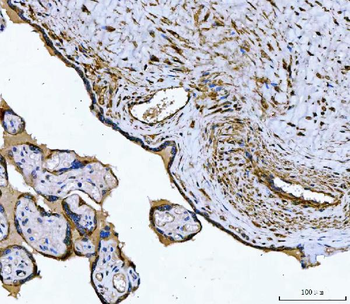
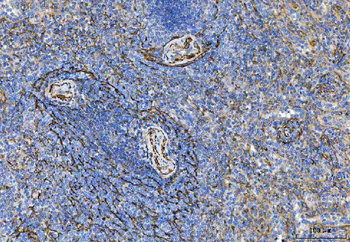
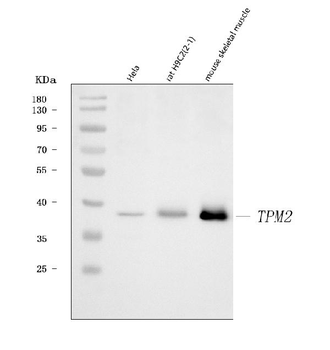
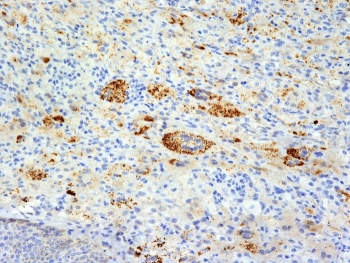
Anti-Tropomyosin 2/TPM2 Antibody [orb1291659]
FC, IF, IHC, WB
Human, Mouse, Rat
Rabbit
Polyclonal
Unconjugated
10 μg, 100 μgHuman TNFSF13B protein [orb705331]
Greater than 93% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
46.6 kDa
Mammalian cell
20 μg, 100 μg, 1 mgHuman TNF protein [orb624131]
Greater than 90% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
19.4 kDa
Yeast
1 mg, 20 μg, 100 μg