You have no items in your shopping cart.
Human IgG (H&L) Antibody Texas Red Conjugated Pre-Adsorbed
Catalog Number: orb347342
| Catalog Number | orb347342 |
|---|---|
| Category | Antibodies |
| Description | Human IgG (H&L) antibody (Texas Red) |
| Species/Host | Donkey |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Tested applications | FC, FLISA, IF |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Immunogen | Human IgG whole molecule |
| Concentration | 1.0 mg/mL |
| Dilution range | FLISA: 1:10,000 - 1:50,000, FC: 1:500 - 1:2,500, IF: 1:1,000 - 1:5,000 |
| Form/Appearance | Lyophilized |
| Purity | This product was prepared from monospecific antiserum by immunoaffinity chromatography using Human IgG coupled to agarose beads followed by solid phase adsorption(s) to remove any unwanted reactivities. Assay by immunoelectrophoresis resulted in a single precipitin arc against anti-Donkey Serum, Human IgG and Human Serum. No reaction was observed against Bovine, Chicken, Goat, Guinea Pig, Hamster, Horse, Mouse, Rabbit, Rat & Sheep Serum Proteins. |
| Conjugation | Texas Red |
| Storage | Store vial at 4° C prior to restoration. For extended storage aliquot contents and freeze at -20° C or below. Avoid cycles of freezing and thawing. Centrifuge product if not completely clear after standing at room temperature. This product is stable for several weeks at 4° C as an undiluted liquid. Dilute only prior to immediate use. |
| Buffer/Preservatives | 0.01% (w/v) Sodium Azide |
| Alternative names | Donkey Anti Human IgG Texas Red Conjugated Antibod Read more... |
| Note | For research use only |
| Application notes | Anti-Human IgG (H&L) Texas Red is designed for immunofluorescence microscopy, fluorescence based plate assays (FLISA) and fluorescent western blotting. This product is also suitable for multiplex analysis, including multicolor imaging, utilizing various commercial platforms. |
| Expiration Date | 12 months from date of receipt. |

Immunostainings with CD68 and VEGF antibodies reveal an increase in expression of both markers at 3 and 7d post operation followed by a decline at d14 and d28. Bevacizumab treatment leads to a reduction of CD68 + cells at d14 and d28 (a). (dashed line: distal tendon stump; asterisk: dermis; scale bar: 200 µm). Bevacizumab is detectable 3d after injection at 4d p.o. (c), but not at 14d p.o. (d). Upon injection at 4 and 11d p.o., Bevacizumab is detectable at 14d p.o. (e). In the vehicle injected tendon, no Bevacizumab is detectable (b).
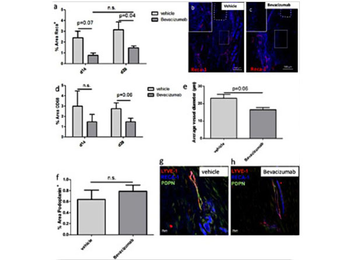
Quantitative analysis of immunofluorescence images shows the capability of Bevacizumab to reduce Reca1+ vessels and CD68-positive cells at 14 and 28d p.o. (a, d), illustrated by representative images (b, c) dashed line: proximal tendon stump. By trend, also the average vessel diameter is reduced in the Bevacizumab group after 28d (e). The density of Podoplanin+ lymphatic vessels is not affected by Bevacizumab (f), as illustrated by representative images taken from the newly formed repair tissue (g, h).
F(ab')2 Human IgG (H&L) Antibody Texas Red Conjugated Pre-Adsorbed [orb348209]
DOT, FC, FLISA, IF
Human
Goat
Polyclonal
Texas Red
1 mgHuman IgG (H&L) Antibody Texas Red Conjugated Pre-Adsorbed [orb347258]
FC, FLISA, IF
Human
Goat
Polyclonal
Texas Red
2 mgHuman IgG (H&L) Antibody Texas Red Conjugated Pre-Adsorbed [orb347319]
FC, FLISA, IF
Human
Rabbit
Polyclonal
Texas Red
2 mgHuman IgG (H&L) Antibody Texas Red Conjugated Pre-Adsorbed [orb347202]
FC, FLISA, IF
Human
Goat
Polyclonal
Texas Red
1 mgF(ab')2 Human IgG IgA IgM (H&L) Antibody Texas Red Conjugated Pre-Adsorbed [orb348172]
FC, FLISA, IF
Human
Goat
Polyclonal
Texas Red
1 mg