You have no items in your shopping cart.
Cav1.2 Antibody: Biotin
Catalog Number: orb148161
| Catalog Number | orb148161 |
|---|---|
| Category | Antibodies |
| Description | Mouse monoclonal to CaV1 (Biotin). 2. Ion channels are integral membrane proteins that help establish and control the small voltage gradient across the plasma membrane of living cells by allowing the flow of ions down their electrochemical gradient. They are present in the membranes that surround all biological cells because their main function is to regulate the flow of ions across this membrane. Whereas some ion channels permit the passage of ions based on charge, others conduct based on an ionic species, such as sodium or potassium. Furthermore, in some ion channels, the passage is governed by a gate which is controlled by chemical or electrical signals, temperature, or mechanical forces. There are a few main classifications of gated ion channels. There are voltage- gated ion channels, ligand- gated, other gating systems and finally those that are classified differently, having more exotic characteristics. The first are voltage- gated ion channels which open and close in response to membrane potential. These are then separated into sodium, calcium, potassium, proton, transient receptor, and cyclic nucleotide-gated channels; each of which is responsible for a unique role. Ligand-gated ion channels are also known as ionotropic receptors, and they open in response to specific ligand molecules binding to the extracellular domain of the receptor protein. The other gated classifications include activation and inactivation by second messengers, inward-rectifier potassium channels, calcium-activated potassium channels, two-pore-domain potassium channels, light-gated channels, mechano-sensitive ion channels and cyclic nucleotide-gated channels. Finally, the other classifications are based on less normal characteristics such as two-pore channels, and transient receptor potential channels. Specifically, Cav1. 2 is a cardiac L-type calcium channel, and is important for excitation and contraction of the heart. It may be associated with a variant of Long QT syndrome called Timothy's syndrome and also with Brugada syndrome. Some references also suggest it is related to bipolar disease as well.... |
| Species/Host | Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Clone Number | S57 |
| Tested applications | ELISA, ICC, IF, IHC, WB |
| Reactivity | Hamster, Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Isotype | IgG1 |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein amino acids 1507-1733 (intracellular carboxyl terminus) of rabbit Cav1.2 |
| Concentration | 1 mg/ml |
| Dilution range | WB (1:1000), IHC (1:1000), ICC/IF (1:100), IP (1:200) |
| Conjugation | Biotin |
| MW | 240kDa |
| Target | Cav1.2 |
| Entrez | 100101555 |
| UniProt ID | P15381 |
| NCBI | NP_001129994.1 |
| Storage | Conjugated antibodies should be stored according to the product label |
| Buffer/Preservatives | 136.36mM Ethanolamine, and 9.55mM Sodium Bicarbonate in 95.45% PBS |
| Alternative names | CACH3 antibody, CACN4 antibody, CACNA 1D antibody, Read more... |
| Note | For research use only |
| Application notes | 1 µg/ml of SMC-300 was sufficient for detection of Cav1.2 in 10 µg of rat brain lysate by colorimetric immunoblot analysis using Goat anti-mouse IgG:HRP as the secondary antibody. |
| Expiration Date | 12 months from date of receipt. |

Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence analysis using Mouse Anti-Cav1.2 Monoclonal Antibody, Clone S57. Tissue: Neuroblastoma cells (SH-SY5Y). Species: Human. Fixation: 4% PFA for 15 min. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-Cav1.2 Monoclonal Antibody at 1:50 for overnight at 4°C with slow rocking. Secondary Antibody: AlexaFluor 488 at 1:1000 for 1 hour at RT. Counterstain: Phalloidin-iFluor 647 (red) F-Actin stain; Hoechst (blue) nuclear stain at 1:800, 1.6mM for 20 min at RT. (A) Hoechst (blue) nuclear stain. (B) Phalloidin-iFluor 647 (red) F-Actin stain. (C) Cav1.2 Antibody (D) Composite.
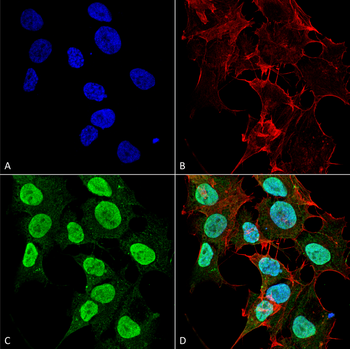
Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence analysis using Mouse Anti-Cav1.2 Monoclonal Antibody, Clone S57. Tissue: Neuroblastoma cell line (SK-N-BE). Species: Human. Fixation: 4% Formaldehyde for 15 min at RT. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-Cav1.2 Monoclonal Antibody at 1:100 for 60 min at RT. Secondary Antibody: Goat Anti-Mouse ATTO 488 at 1:200 for 60 min at RT. Counterstain: Phalloidin Texas Red F-Actin stain; DAPI (blue) nuclear stain at 1:1000, 1:5000 for 60 min at RT, 5 min at RT. Localization: Cell Membrane, Membrane, Cytoplasm, Nucleoplasm. Magnification: 60X. (A) Phalloidin Texas Red F-Actin stain; DAPI (blue) nuclear stain. (B) Anti-Cav1.2 Antibody. (C) Composite. (A) DAPI (blue) nuclear stain. (B) Phalloidin Texas Red F-Actin stain. (C) Cav1.2 Antibody. (D) Composite.
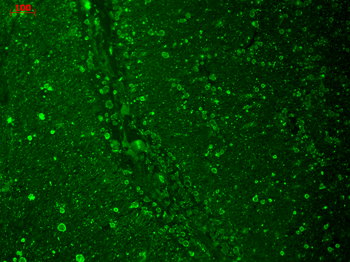
Immunohistochemistry analysis using Mouse Anti-CaV1.2 Calcium Channel Monoclonal Antibody, Clone S57. Tissue: hippocampus. Species: Human. Fixation: 10% formalin. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-CaV1.2 Calcium Channel Monoclonal Antibody at 1:100 for 1 hour at RT. Secondary Antibody: FITC Goat Anti-Mouse (green) at 1:50 for 1 hour at RT.
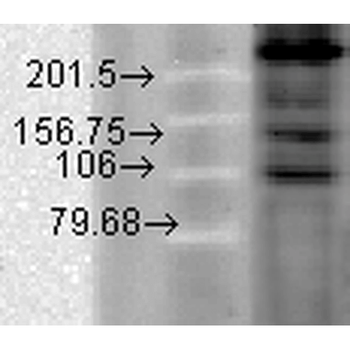
Western Blot analysis of Hamster T-CHO cell lysate showing detection of CaV1.2 Calcium Channel protein using Mouse Anti-CaV1.2 Calcium Channel Monoclonal Antibody, Clone S57. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-CaV1.2 Calcium Channel Monoclonal Antibody at 1:1000.
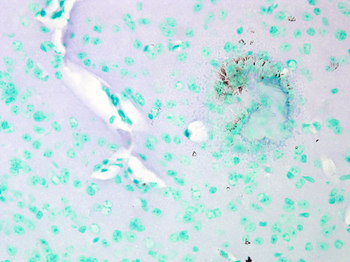
Immunohistochemistry analysis using Mouse Anti-CaV1.2 Calcium channel Monoclonal Antibody, Clone S57. Tissue: Brain Tissue. Species: Mouse. Fixation: Formalin. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-CaV1.2 Calcium channel Monoclonal Antibody at 1:10000 for 12 hours at 4°C. Secondary Antibody: Biotin Goat Anti-Mouse at 1:2000 for 1 hour at RT. Counterstain: Mayer Hematoxylin (purple/blue) nuclear stain at 200 μl for 2 minutes at RT. Magnification: 40x.
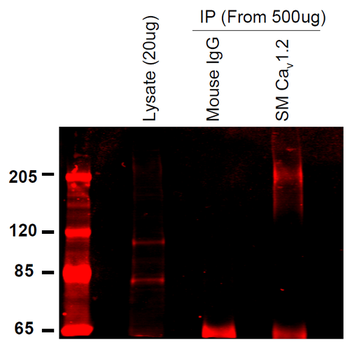
Immunoprecipitation analysis using Mouse Anti-CaV1.2 Calcium Channel Monoclonal Antibody, Clone S57. Tissue: INS-1E cells. Species: Rat. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-CaV1.2 Calcium Channel Monoclonal Antibody at 1:200.
CACNA1C Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Biotin) [orb458121]
ELISA, IF, IHC-Fr, IHC-P
Bovine, Canine, Equine, Human, Mouse, Porcine, Rabbit, Rat
Rabbit
Polyclonal
Biotin
100 μlCACNA1C Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Biotin) [orb458144]
ELISA, IF, IHC-Fr, IHC-P
Bovine, Canine, Equine, Human, Mouse, Porcine, Rabbit, Rat
Rabbit
Polyclonal
Biotin
100 μl



