You have no items in your shopping cart.
AHA1 antibody
Catalog Number: orb345571
| Catalog Number | orb345571 |
|---|---|
| Category | Antibodies |
| Description | AHA1 antibody |
| Species/Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Tested applications | ELISA, IHC, WB |
| Reactivity | Human, Monkey |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Immunogen | This affinity purified antibody was prepared from whole rabbit serum produced by repeated immunizations with a synthetic peptide corresponding to an internal region of human AHA1 protein. |
| Concentration | 1.0 mg/mL |
| Dilution range | ELISA: 1:35,000 - 1:185,000, IHC: User Optimized, WB: 1 µg/mL |
| Form/Appearance | Liquid (sterile filtered) |
| Purity | This affinity purified antibody is directed against human AHA1 protein. The product was affinity purified from monospecific antiserum by immunoaffinity chromatography. A BLAST analysis was used to suggest cross-reactivity with AHA1 protein from human and chimpanzee based on 100% homology with the immunizing sequence. Reactivity against homologues from other sources is not known. |
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| UniProt ID | O95433 |
| NCBI | NP_001308370.1 |
| Storage | Store vial at -20° C prior to opening. Aliquot contents and freeze at -20° C or below for extended storage. Avoid cycles of freezing and thawing. Centrifuge product if not completely clear after standing at room temperature. This product is stable for several weeks at 4° C as an undiluted liquid. Dilute only prior to immediate use. |
| Buffer/Preservatives | 0.01% (w/v) Sodium Azide |
| Alternative names | rabbit anti-AHA1 Antibody, Aha-1, Aha 1, Ahsa1 ant Read more... |
| Note | For research use only |
| Application notes | This affinity purified antibody has been tested for use in ELISA and western blotting. Specific conditions for reactivity should be optimized by the end user. Expect a band approximately 38-40 kDa in size corresponding to AHA1 protein by western blotting in the appropriate cell lysate or extract. |
| Expiration Date | 12 months from date of receipt. |
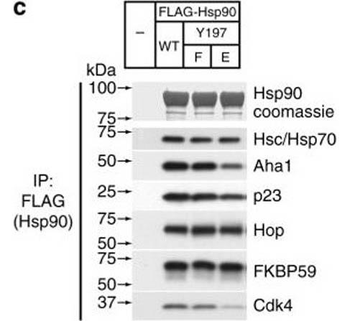
Assembly of complexes of Cdc37 and Hsp90 phosphomimetic variants with clients and cochaperones. a Binary complex formation between Cdc37 variants and bRaf (left), and between Hsp90β variants and Cdc37 (right), followed by ITC. The corresponding Kd values are displayed in the inset. Error bars in the Kd values correspond to the errors resulted in fitting of the data into a single binding site model. b HEK-293 cells were cotransfected with indicated HA-tagged Cdc37 and FLAG-tagged bRaf plasmids. After cell lysis, proteins were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG resin for 1 h at 4 °C with rotation. Bead pellets were washed and analyzed for Cdc37 interaction by SDS-PAGE/western blot, using anti-HA antibody. c HEK-293 cells were transfected with FLAG-tagged Hsp90, Hsp90Y197E, or Hsp90Y197F plasmids. After cell lysis, proteins were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG resin for 1 h at 4 °C with rotation. Bead pellets were washed three times before analysis by SDS-PAGE/western blot. Co-precipitating endogenous Hsp70, Aha1, p23, Hop, Fkbp59, and Cdk4 were detected with specific antibodies. d HEK-293 cells were transfected with the indicated Hsp90, androgen receptor (AR), and glucocorticoid receptor (GR) plasmids. Proteins were precipitated with GFP-Trap resin (left) or ANTI-FLAG M2 agarose (right) for 1 h at 4 °C with rotation. Bead pellets were washed three times with lysis buffer before analysis by SDS-PAGE/western blot as indicated. AR was visualized with anti-GFP antibody, GR was visualized with a specific antibody, and Hsp90 was visualized with anti-FLAG antibody .
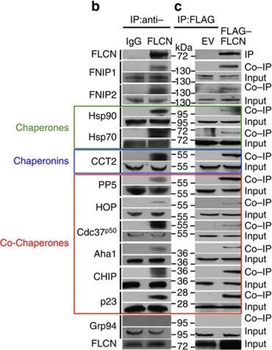
Folliculin is a new client of Hsp90. (a) FLAG–FLCN was expressed and isolated from HEK293 cells. Profile of interacting proteins determined by MALDI–time of flight. Red nodes represent chaperones and co-chaperones, blue nodes are chaperonins and green nodes are splicing factors and ribosomal proteins. (b) FLCN was isolated from HEK293 cell lysates using anti-FLCN or IgG (control) and immunoblotted with indicated antibodies to confirm protein interactions. (c) HEK293 cells were transiently transfected with FLAG–FLCN or empty vector control (EV), immunoprecipitated and immunoblotted with indicated antibodies to confirm interacting proteins. (d) HEK293 cells were treated with 10 μM of the Hsp70 inhibitor JG-98 at the indicated time points. FLCN protein stability in soluble and insoluble fraction was assessed by immunoblotting. (e) HEK293 cells were treated with 1 μM GB at the indicated time points. FLCN protein stability was assessed by immunoblotting. Akt and Phospho-S473-Akt were used as positive controls. (f) Hsp90α–FLAG was transiently expressed in HEK293 cells. Cells were treated with 1 μM GB for the indicated times. Hsp90α–FLAG was immunoprecipitated and co-IP of FLCN was examined by immunoblotting. (g) HEK293 cells were treated with 50 nM of the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib (BZ) for the indicated times. FLCN protein levels were evaluated at the indicated time points by immunoblotting (upper blots). HEK293 cells were also treated with 1 μM GB for 1 h before addition of 50 nM BZ. Immunoblotting was used to evaluate the FLCN level for the indicated time points (lower blots). (h) Empty vector (EV) or FLAG–FLCN was used to transiently transfect HEK293 cells for 24 h then treated for 4 h with either 50 nm BZ or 1 μM GB. FLAG–FLCN was immunoprecipitated and ubiquitination was examined by immunoblotting with a pan-anti-ubiquitin antibody.
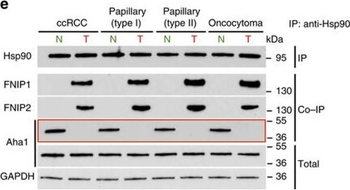
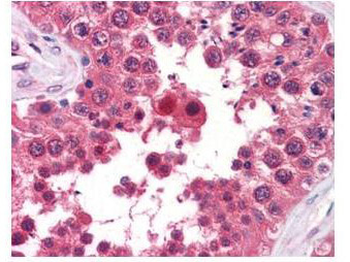
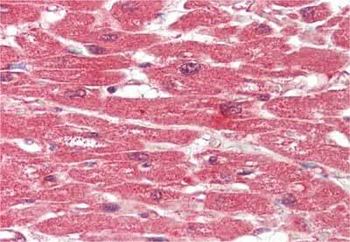
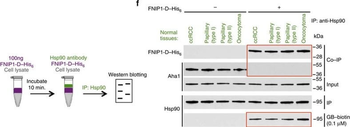
High levels of FNIPs make renal tumours sensitive to Hsp90 inhibitor GB. (a) Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC), (b) Papillary type I, (c) Papillary type II, (d) Oncocytoma (Tumours, T) and adjacent normal tissues (Normal, N) were stained with haematoxylin and eosin (H&E). Proteins were also extracted from these tumours and adjacent normal tissues and incubated with indicated amounts of biotinylated GB followed by streptavidin agarose beads. Hsp90 was detected by immunoblotting. Expression of FNIP1 and FNIP2 in these samples was also detected by immunoblotting. (e) Hsp90 immunoprecipitated from tumours (T) and adjacent normal tissues (N) in a–d. Co-IP of FNIPs and Aha1 was examined by immunoblotting. (f) Lysates from normal tissues in a–d were incubated with or without 100 ng of pure FNIP1-D–His6 for 10 min. Hsp90 was immunoprecipitated and co-IP of FNIP1-D–His6 and Aha1 were shown by immunoblotting.
High levels of FNIPs make renal tumours sensitive to Hsp90 inhibitor GB. (a) Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC), (b) Papillary type I, (c) Papillary type II, (d) Oncocytoma (Tumours, T) and adjacent normal tissues (Normal, N) were stained with haematoxylin and eosin (H&E). Proteins were also extracted from these tumours and adjacent normal tissues and incubated with indicated amounts of biotinylated GB followed by streptavidin agarose beads. Hsp90 was detected by immunoblotting. Expression of FNIP1 and FNIP2 in these samples was also detected by immunoblotting. (e) Hsp90 immunoprecipitated from tumours (T) and adjacent normal tissues (N) in a–d. Co-IP of FNIPs and Aha1 was examined by immunoblotting. (f) Lysates from normal tissues in a–d were incubated with or without 100 ng of pure FNIP1-D–His6 for 10 min. Hsp90 was immunoprecipitated and co-IP of FNIP1-D–His6 and Aha1 were shown by immunoblotting.
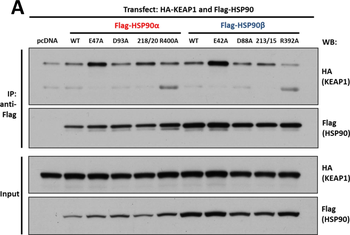
Interaction of KEAP1 and RHOBTB2 with HSP90 isoforms. (A) KEAP1interaction with HSP90 WT and mutants: HEK293 cells transfected with HA-KEAP1 and each FLAG-HSP90 construct were harvested, immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG beads and western blotted for HA. Input lysates were normalized and run as controls. (B) RHOBTB2 interaction with HSP90 WT and mutants: HEK293 cells transfected with HA-RHOBTB2 and each FLAG-HSP90 construct were harvested, immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG beads and western blotted for HA. Input lysates were normalized and run as controls. (C) Measurement of the relative interaction strength of KEAP1 and RHOBTB2 with each HSP90 isoform by LUMIER: HEK293 cells transfected with KEAP1 or RHOBTB2 and each HSP90 isoform were harvested, applied to a 96-well anti-FLAG plate and assayed for luciferase activity. The difference in relative interaction strength of HSP90α and HSP90β for KEAP1 and RHOBTB2 (each approximately 3-fold) was statistically significant (p < 0.05).
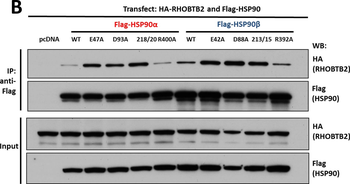
Interaction of KEAP1 and RHOBTB2 with HSP90 isoforms. (A) KEAP1interaction with HSP90 WT and mutants: HEK293 cells transfected with HA-KEAP1 and each FLAG-HSP90 construct were harvested, immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG beads and western blotted for HA. Input lysates were normalized and run as controls. (B) RHOBTB2 interaction with HSP90 WT and mutants: HEK293 cells transfected with HA-RHOBTB2 and each FLAG-HSP90 construct were harvested, immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG beads and western blotted for HA. Input lysates were normalized and run as controls. (C) Measurement of the relative interaction strength of KEAP1 and RHOBTB2 with each HSP90 isoform by LUMIER: HEK293 cells transfected with KEAP1 or RHOBTB2 and each HSP90 isoform were harvested, applied to a 96-well anti-FLAG plate and assayed for luciferase activity. The difference in relative interaction strength of HSP90α and HSP90β for KEAP1 and RHOBTB2 (each approximately 3-fold) was statistically significant (P< 0.05).
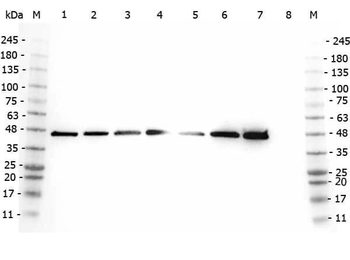
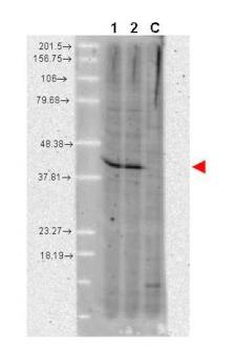
Western Blot of Rabbit anti-AHA1 antibody. Marker: Opal Pre-stained ladder. Lane 1: HEK293 lysate (p/n orb348669). Lane 2: HeLa Lysate (p/n orb348668). Lane 3: MCF-7 Lysate (p/n orb348664). Lane 4: Jurkat Lysate. Lane 5: A431 Lysate (p/n orb348665). Lane 6: Raji Lysate (p/n orb348672). Lane 7: Ramos Lysate. Lane 8: NIH/3T3 Lysate (p/n orb348714). Load: 35 µg per lane. Primary antibody: AHA1 antibody at 1:2000 for overnight at 4°C. Secondary antibody: Peroxidase rabbit secondary antibody (p/n orb347654) at 1:30000 for 60 min at RT. Blocking Buffer: 1% Casein-TTBS for 30 min at RT. Predicted/Observed size: 38 kDa, 38 kDa for AHA1.
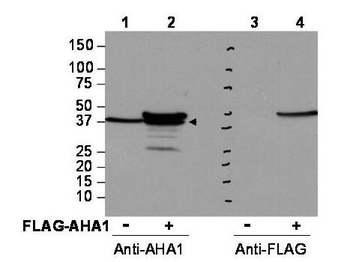
Western blot using Biorbyt's affinity purified anti-AHA1 antibody shows detection of AHA1 in Cos7 cells. For Lanes 2 and 4, Cos7 cells were transfected with pcDNA3-FLAG-AHA1. For Lanes 1 and 3, Cos7 cells were not transfected. Extracts (40 µg per lane) were electrophoresed and transferred to nitrocellulose. The membrane was probed with anti-AHA1 (lanes 1 and 2, 1:2000 dilution) or anti-FLAG (lanes 3 and 4). The lower band seen in anti-AHA1 blotting (arrowhead) is endogenous AHA1.
AHA1/AHSA1 Antibody [orb1145840]
ELISA, FC, ICC, IF, IHC, WB
Human, Mouse, Rat
Rabbit
Polyclonal
Unconjugated
10 μg, 100 μg
Filter by Rating
- 5 stars
- 4 stars
- 3 stars
- 2 stars
- 1 stars